 Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial Resistance
The call funded 11 projects to develop innovative solutions to combat antimicrobial resistance.
Challenge
Appropriate antibiotic use has the power to save lives in the most vulnerable communities, and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) impacts multiple global health priority areas: HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, maternal and neonatal health, pneumonia, and enteric and diarrheal diseases. It is critical to better understand the prevalence of AMR and its impact on mortality in developing countries so that access to appropriate antibiotics is ensured while inappropriate use of antibiotics is limited. In particular, there is a need to better understand resistance in bacterial infections of newborns and young children – and to this end, understanding what is the prevalence of AMR in the community, how it impacts mortality, and how it impacts health targets. Tackling AMR will require a global, coordinated approach and the linking together of different research communities for new perspectives on the problem.
Goal
The program pursued new approaches with the potential to transform public health action on a regional or global scale by identifying and filling gaps in knowledge on the burden of resistance to antibacterial agents.
Specifically, the financed projects proposed innovation in the following areas:
- Data sources: Pilot tests of new sources of data, particularly those that would bring together different research communities from different disciplines for new perspectives on the problem;
- Analytical methods: Pilot tests of bioinformatics approaches, including new ways to analyze, combine or connect existing databases;
- Biomarkers: Pilot tests of new biomarkers or combinations of biomarkers that could lead to a new understanding of the actionable implications of antimicrobial resistance surveillance data;
- Low-cost technologies and products: Exploratory work in developing new technologies and products, including:
- those that specifically target improved infection prevention and control in healthcare settings to reduce reliance on healthcare provider behavior change, and
- technologies to remove antibiotics from effluents.
Projects in Antimicrobial Resistance

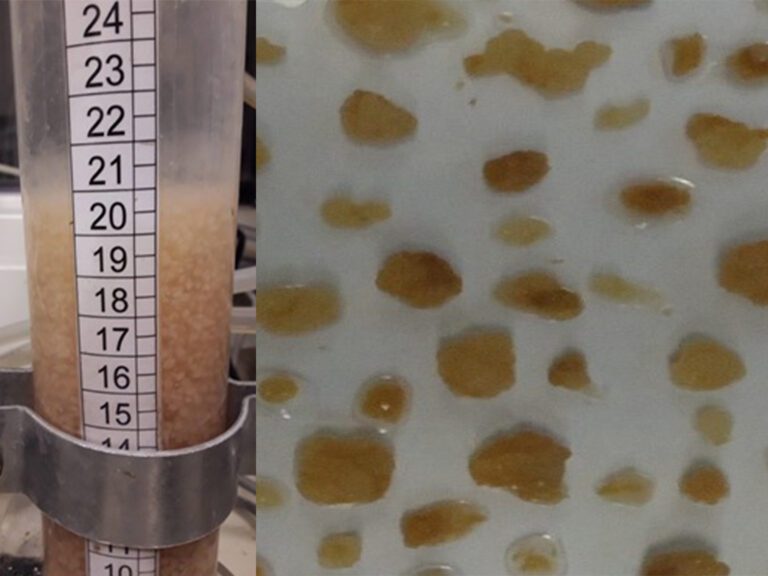
The use of low-cost immobilized DNA aptamers on cellulose filter to remove antibiotic residues from effluents

The dynamics of circulation of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms between livestock operations and hospitals
OneBR: integrated genomic database for surveillance, diagnosis, management, and treatment of antimicrobial resistance in the human-animal-environment interface
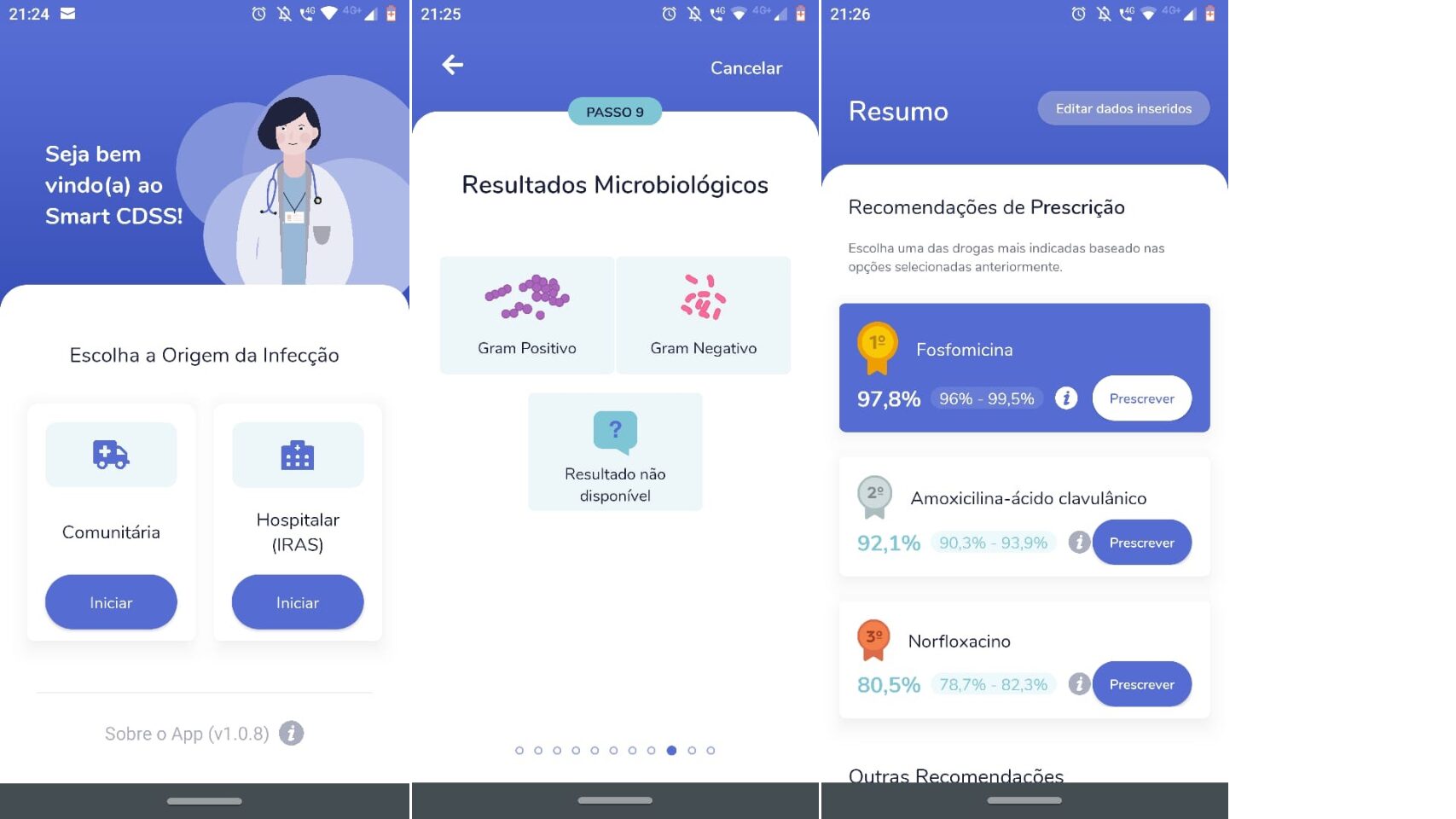
SMART-EP, an artificial intelligence system to strengthen antimicrobial prescription in a children's hospital

Monitoring of antimicrobial resistance in uropathogens from community residents and genetic correlation with isolated resistance determinants from Enterobacterales present in meat consumption
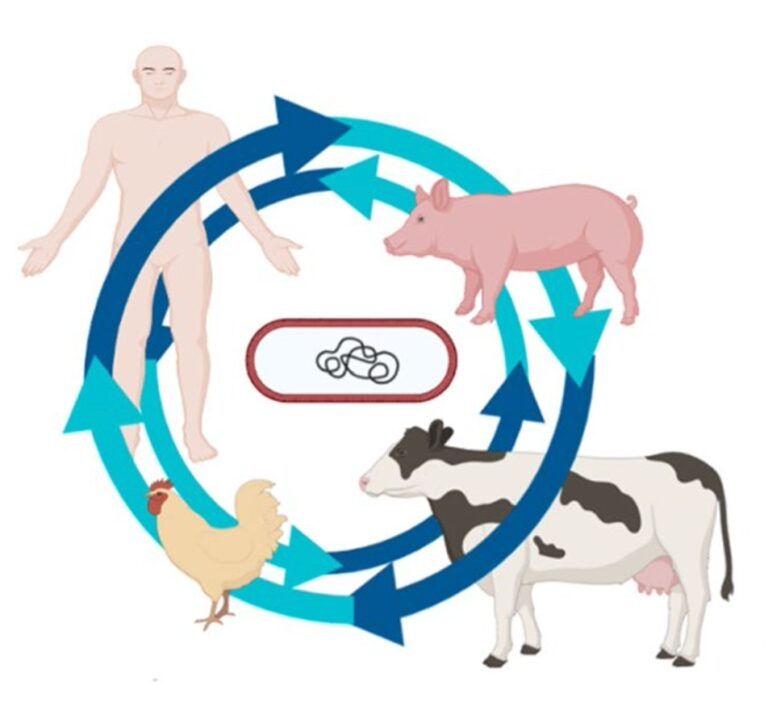
Application of metagenomic analysis to the detection of EsβL- and carbapenemase-producing enteric pathogens recovered from different hosts
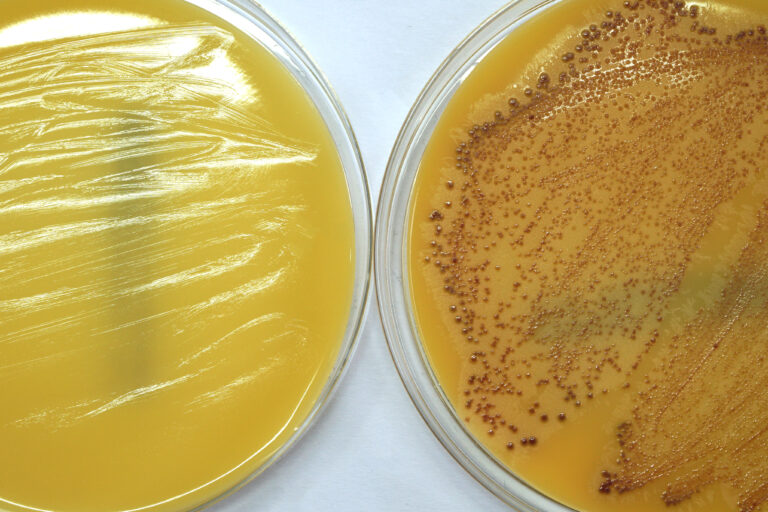
Tracking methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) evolution to discover important biomarkers for rapid characterization of unique MRSA clones in hospital bloodstream infections

Data science on drug-resistant tuberculosis in Brazil

Application of low-cost and sustainable solar oxidation treatment to prevent microbial resistance in effluents in Brazil

Plasmid curing by an Ethiopian barley: a natural feed/food approach to reduce plasmid mediated antibiotic resistance
Latest studies published in Antimicrobial Resistance
- Pillonetto M, Kalil A, Becker G, Giamberardino AL, Teixeira B, Bergamo R, Madeira H, Dias V, Miorando, Giglio R. (2020). SMART-CDSS An artificial intelligence system for antimicrobial prescription support. Gates Open Res, 4. https://doi.org/10.21955/gatesopenres.1116684.1) - 10/2023
- Human pandemic K27-ST392 CTX-M-15 extended-spectrum β-lactamase-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae: A one health clone threatening companion animals - 12/2022
- Challenges on solar oxidation as post-treatment of municipal wastewater from UASB systems: Treatment efficiency, disinfection and toxicity - 12/2022
- Exploring the Bacteriome and Resistome of Humans and Food-Producing Animals in Brazil - 08/2022
- World Health Organization critical priority Escherichia coli clone ST648 in magnificent frigatebird (Fregata magnificens) of an uninhabited insular environment - 08/2022
- Solar photo-Fenton mediated by alternative oxidants for MWWTP effluent quality improvement: Impact on microbial community, priority pathogens and removal of antibiotic-resistant genes - 08/2022
- Different Swine Production Systems Can Shape Slurry Resistome at Mechanism and Class Levels Based on Swine Manure Evaluation - 07/2022
- Large Scale Genome-Centric Metagenomic Data from the Gut Microbiome of Food-Producing Animals and Humans - 06/2022
- Genomic Analysis of a Highly Virulent NDM-1-Producing Escherichia coli ST162 Infecting a Pygmy Sperm Whale (Kogia breviceps) in South America - 06/2022
- Genomic insights of high-risk clones of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolated from community infections and commercial meat in southern Brazil - 06/2022
- Genomic insights of high-risk clones of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolated from community infections and commercial meat in southern Brazil - 06/2022
- Phylogenomic analysis of CTX-M-15–producing Enterobacter hormaechei belonging to the high-risk ST78 from animal infection: another successful One Health clone? - 06/2022
- Susceptibility to first choice antimicrobial treatment for urinary tract infections to Escherichia coli isolates from women urine samples in community South Brazil - 06/2022